Spring / Spring Boot
Spring Boot is a framework for building and running Spring applications by providing defaults for code and annotation configuration to quick start new Spring projects within no time. It follows "Opinionated Defaults Configuration" Approach to avoid lot of boilerplate code and configuration to improve Development, Unit Test and Integration Test Process.
One of the biggest challenges faced by the Spring developers is that amount of time they spent on configuring and bootstarting their spring applications.With growing number of frameworks with Spring community, it is necessary to have a common framework that solves the configurations. Spring Boot simply scan the classpath and add the required libraries from various repositories. This improves the productivity and saves lot of time for the developers.
To ease the Java-based applications Development, Unit Test and Integration Test Process.
To reduce development, unit Test and integration Test time by providing some defaults.
To increase productivity.
It avoids writing lots of boilerplate code, annotations and XML configuration.
It is very easy to integrate Spring Boot Application with its Spring Ecosystem like Spring JDBC, Spring ORM, Spring Data, Spring Security etc. It follows the "Opinionated Defaults Configuration" approach to reduce developer effort.
It provides Embedded HTTP servers like Tomcat, Jetty etc. to develop and test our web applications very easily.
It provides CLI (Command Line Interface) tool to develop and test Spring Boot(Java or Groovy) Applications from command prompt very easily and quickly.
It provides plugins to develop and test Spring Boot Applications very easily using build Tools like Maven and Gradle.
It provides plugins to work with embedded and in-memory Databases very easily.
We can convert all kinds of spring projects into Spring Boot Applications however it is time consuming process to convert existing or legacy Spring Framework projects into Spring Boot Applications.
No. Spring Boot is limited to work with Spring based applications (Java/groovy).
2.2.1 is the latest version.
CommandLineRunner Interface is used to indicate that a bean should run when it is contained within a Spring application. Multiple CommandLineRunner beans can be defined within the same application context and can be ordered using the Ordered interface or @Order annotation.
Both are similar in terms of functionality and the difference is that If you need access to ApplicationArguments instead of the raw String array consider using ApplicationRunner than CommandLineRunner.
Micro service is an architectural style that structures an application as a collection of loosely coupled services, which implement business capabilities. The microservice architecture enables the continuous delivery/deployment of large, complex applications. It also enables an organization to evolve its technology stack.
The components are,
- Spring Boot Starter,
- Spring Boot AutoConfigurator,
- Spring Boot Actuator,
- Spring Boot CLI,
- Spring Boot IDE,
- and Spring Boot Initilizr.
Configuration file used in Spring boot projects is application.properties. It is used to override all default configurations.
Spring boot actuator is one of the important features of Spring boot. It is used to access the current state of running applications in a production environment. There are various metrics that you can use to check the current state of the application.
Spring boot actuator provides restful web services end points which you can simply use and check various metrics. For example, /metrics end point will display metrics such as free memory, processors, uptime, and other properties.
Spring boot supports embedded containers such as Tomcat (default), Jetty and undertow servers.
Spring Boot Initializr is a Spring Boot tool to bootstrap Spring Boot or Spring Applications easily.
Spring Boot Initializr is available in the below forms:
- Spring Boot Initializr With Web Interface,
- Spring Boot Initializr With IDEs/IDE Plugins,
- Spring Boot Initializr With Spring Boot CLI,
- Spring Boot Initializr With ThirdParty Tools.
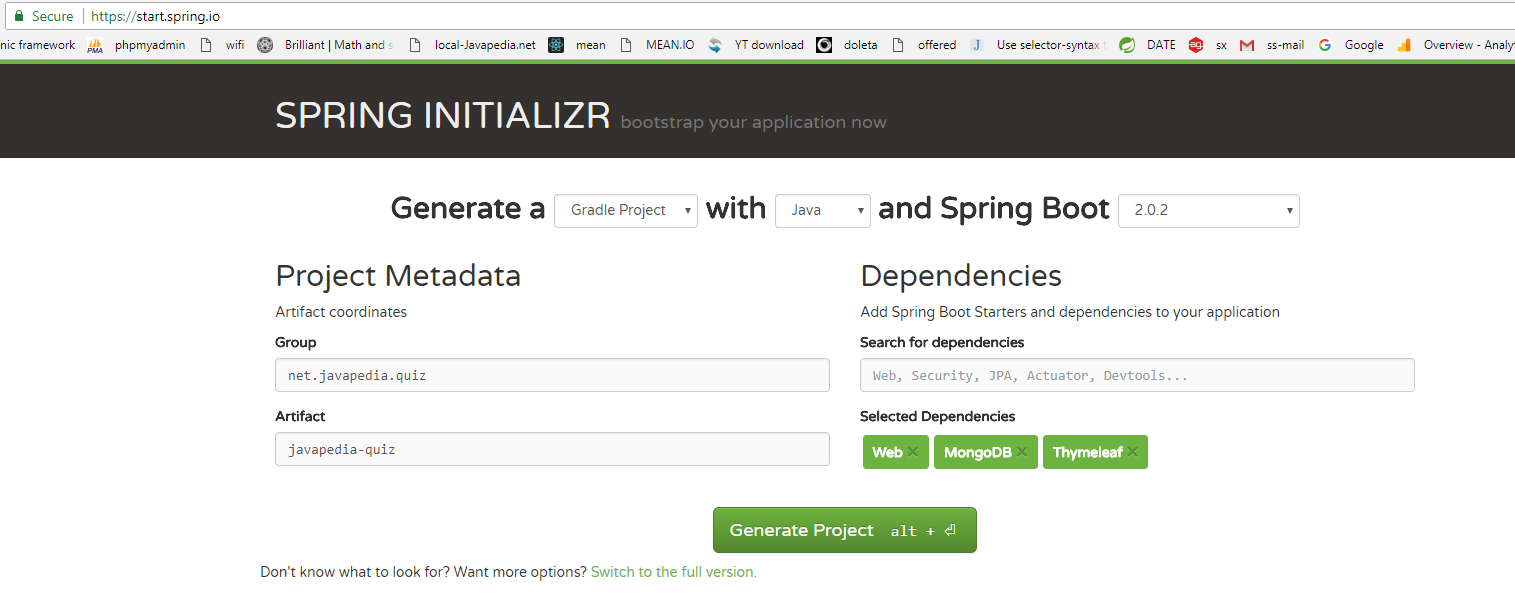
A demo of the spring initializr web interface is available here.
Spring Boot provides the @SpringBootTest annotation for writing Unit Test Cases.
Create a folder called static under resources folder and put your static content in that folder. For your example the path to myStatic.js would be resources\static\js\myStatic.js.
You may refer to it in jsp as shown below.
<script src="/js/myStatic.js"></script>
You may change the port in spring boot by adding a property server.port = <port> in application.properties file.
Spring Boot Starters are a set of convenient dependency descriptors that you can include in your application. You get all the Spring and related technology at one-stop-shop that you need without having to deal with sample code and copy paste loads of dependency descriptors. It minimizes the effort.
For example, to work with Spring & JPA for database access project include only the spring-boot-starter-data-jpa dependency in your project POM.
spring-boot-starter-data-jpafor Spring Data JPA.spring-boot-starter-webfor Spring Web applcation and creating Restful services.spring-boot-starter-securityfor Spring security.spring-boot-starter-testfor unit testing your application.spring-boot-starter-batchfor creating spring batch jobs.
Please find the complete list of spring boot starters here.
Spring boot may include dependencies that are not used thereby causing huge deployment file size.
Turning legacy spring applications into Spring boot requires a lot of effort and a time-consuming process.
Limited control of your application.
Use Spring boot starter spring-boot-starter-activemq dependency in your applcation POM xml file and it takes care of all dependencies and configuration required for activeMQ projects.
Under application.properties add a property spring.activemq.broker-url along with the URL to configure external ActiveMQ in your application.
Using Spring Boot Dev Tools module we can achieve auto reload. It is a powerful tool that helps developers to lessen the development cycle and enable easy deployment and testing during development.
To enable this feature, add the below dependency to Maven POM file.
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies>
The below configuration is for Gradle:
configurations { developmentOnly runtimeClasspath { extendsFrom developmentOnly } } dependencies { developmentOnly("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-devtools") }
The banner that is printed on start up can be changed by adding a banner.txt file to your classpath or by setting the spring.banner.location property to the location. In addition to a text file, you can also add a banner.gif, banner.jpg, or banner.png image file to your classpath or set the spring.banner.image.location property. Images are converted into an ASCII art representation and printed above any text banner.
When upgrading Spring boot, some properties may have been renamed or removed. Spring Boot provides a way to analyze your application's environment and print diagnostics at startup, but also temporarily migrate properties at runtime. To enable that feature, add the following dependency to your project:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-properties-migrator</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency>
Once you're done with the migration, remove this module from your project's dependencies.
To create an executable jar, add the spring-boot-maven-plugin to our pom.xml. Insert the following lines just below the dependencies section in your project's POM.xml:
<build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
It is possible to get Spring Boot to work with other build systems such as Ant, but they are not well supported. It is recommended to use with Gradle or Maven.
Tomcat is the default embedded container when we specify web since spring-boot-starter-web dependency declares spring-boot-starter-tomcat as its dependency.
To change from tomcat to Jetty, we need to remove tomcat dependency by specifying the exclusion in pom.xml if you are using maven.
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency>
After removing the tomcat dependency, the next step is to specify the dependency for jetty.
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId> </dependency>
Now build your project using maven and run your application to see that jetty in use.
The default tomcat port is 8080. To change it, specify the server.port property with desired port in the application properties or yaml.
application.properties:
server.port=8091
application.yml:
server: port: 8091
Alternatively, you may pass the property as JVM option as -Dserver.port=8091.
@SpringBootApplication annotation can be used to enable those three features below.
@EnableAutoConfigurationenable Spring Boot's auto-configuration mechanism.@ComponentScanenable @Component scan on the package where the application is located.@Configurationallow to register extra beans in the context or import additional configuration classes.
The @SpringBootApplication annotation is equivalent to using @Configuration, @EnableAutoConfiguration, and @ComponentScan with its default attributes.
package net.javapedia.springboot.example; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication // same as using @Configuration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan public class MyApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args); } }
Yes, the Spring Boot Maven plugin includes a run goal that is used to quickly compile and run your application.
mvn spring-boot:run
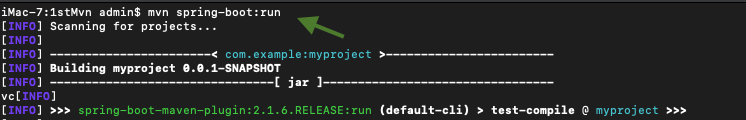
Similarly, Spring Boot Gradle plugin also includes a bootRun task that can be used to run your application
gradle bootRun
- Property Defaults: spring-boot-devtools module automatically applies sensible development-time configuration by disabling properties such as caching to false during development; Sets DEBUG mode for web logging group which helps get more information about incoming request.
- Automatic Restart: Applications that use spring-boot-devtools restart automatically whenever files on the classpath change. This can be a useful feature when working in an IDE, as it restarts automatically with the code changes.
- Live Reload: The spring-boot-devtools module includes an embedded LiveReload server that can be used to trigger a browser refresh when a resource is changed.
- Global Settings: You can configure global devtools settings by adding a file named .spring-boot-devtools.properties to your $HOME folder. Any properties added to this file apply to all Spring Boot applications on your machine that use devtools.
- Remote Applications: spring-boot-devtools provides out of the box remote debugging capabilities via HTTP, to have this feature it is required that spring-boot-devtools are packaged as part of the application. This can be achieved by disabling excludeDevtools configuration in the plugin in maven.
Spring boot automatically configures a lot of dependencies just by its availability in the classpath. For example, it can auto configure tomcat if the server container is not available. This is why spring boot is opinionated because it auto-configure many dependencies if it is not needed and we can override auto-configuration settings as needed.
Auto configuration is disabled by default and use one of the annotations @SpringBootApplication or @EnableAutoConfiguration on the Main class to enable the feature.
Starter dependencies combine many libraries into one based on its functionality/dependency and acts as a single starter package.
It eliminates the need to manually add dependencies in build script and also manages compatibility and version mismatch issues.
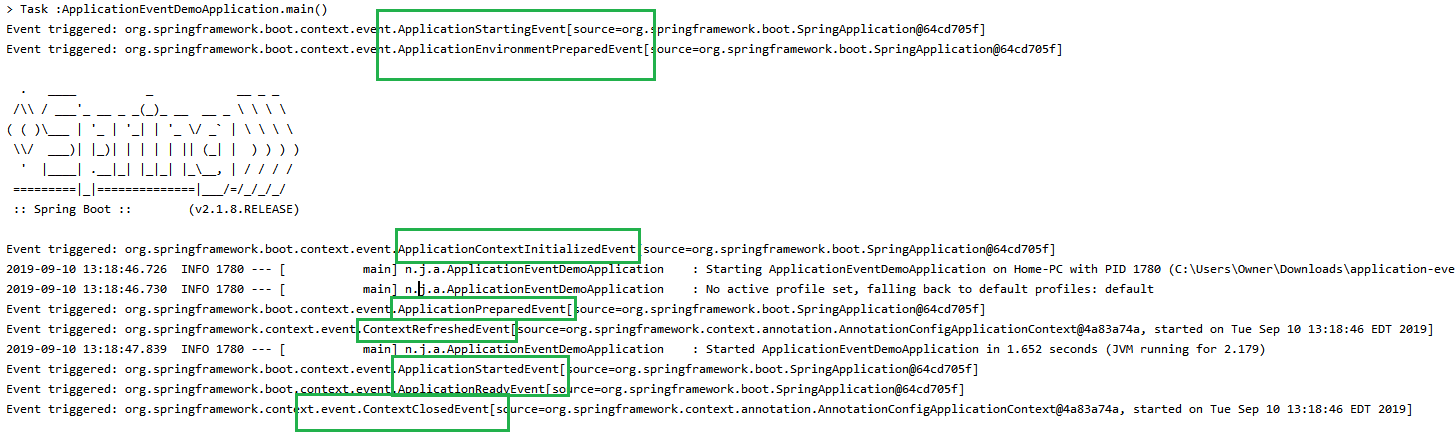
An ApplicationStartingEvent is sent at the start of a run but before any processing, except for the registration of listeners and initializers.
An ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent is sent when the Environment to be used in the context is known but before the context is created.
An ApplicationPreparedEvent is sent just before the refresh is started but after bean definitions have been loaded..
An ApplicationStartedEvent is sent after the context has been refreshed but before any application and command-line runners have been called.
An ApplicationReadyEvent is sent after any application and command-line runners have been called. It indicates that the application is ready to service requests.
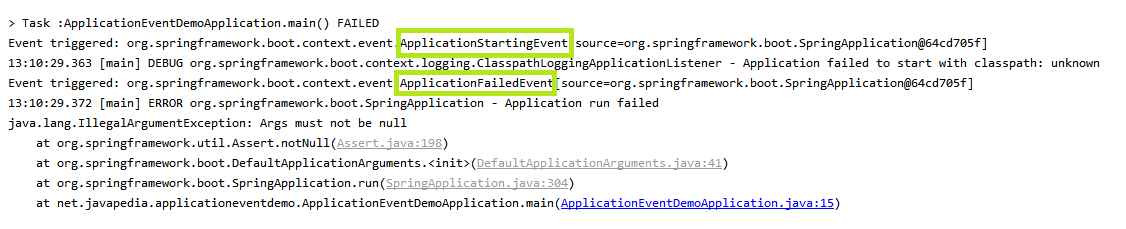
An ApplicationFailedEvent is sent if there is an exception on startup.
package net.javapedia.applicationeventdemo; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; @SpringBootApplication public class ApplicationEventDemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication myApp = new SpringApplication(ApplicationEventDemoApplication.class); myApp.addListeners(new MyApplicationListener()); myApp.run(args); } static class MyApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> { @Override public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { System.out.println("Event triggered: " + event ); } } }
Example for ApplicationFailedEvent
package net.javapedia.applicationeventdemo; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; @SpringBootApplication public class ApplicationEventDemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication myApp = new SpringApplication(ApplicationEventDemoApplication.class); myApp.addListeners(new MyApplicationListener()); myApp.run(null); } static class MyApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> { @Override public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { System.out.println("Event triggered: " + event ); } } }
Thymeleaf is a server-side Java template engine for web applications to bring elegant natural templates for your web apps.
It is easy to integrate with spring Framework and works well with HTML5 Java-based web applications.
In order to use thymeleaf in your project, add the dependency in your project's dependency as shown below.
Maven:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> <version>2.1.9.RELEASE</version> </dependency>
Gradle:
compile group: 'org.springframework.boot', name: 'spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf', version: '2.1.9.RELEASE'
The Spring Boot restart technology works by using 2 classloaders.
Class that don't change ( 3rd party jars, as an example) are loaded into base classloader. Classes that actively change during development are loaded into restart classloader.
When the application restarts, the restart classloader is destroyed and new one is created. This makes the application restarts faster than "cold restart" as the base loader is already available.
WebApplicationType is an enumeration that represent possible types of web application.
- NONE: The application is NOT an web application and should not start an embedded web server.
- REACTIVE: The application should run as a reactive web application and should start an embedded reactive web server.
- SERVLET: The application should run as a servlet-based web application and should start an embedded servlet web server.
We may call setWebApplicationType(WebApplicationType.NONE) , for example, to choose the type as needed.
Both interfaces, CommandLineRunner and ApplicationRunner works in the same way and offers a single run method.
The difference is, the CommandLineRunner interface provides access to the application arguments as a simple String array, while ApplcationRunner uses the ApplicationArguments interface, which provides access to both the raw String[] arguments as well as parsed option and non-option arguments.
Find more information here.
The EnvironmentPostProcessor interface allows us to manipulate the Environment before even the application starts. This interface allows us to create support for encrypting/decrypting property values/ add new properties etc.
Spring Boot uses commons-logging and LogBack implementation by default.
This question is already answered here.
You may enable auto-reload of spring boot application by adding the spring-boot-devtools dependency in the pom.xml file.
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> <optional>true </dependency>
As per wikipedia, Hypermedia as the Engine of Application State (HATEOAS) is a component of the REST application architecture that distinguishes it from other network application architectures. With HATEOAS, a client interacts with a network application which provide information dynamically through hypermedia. A REST client needs little to no prior knowledge about how to interact with an application or server beyond a generic understanding of hypermedia.
the JSON representation of the resource will be enriched with a list of hypermedia elements in a _links property. One form of this is a link pointing to the resource itself as shown below.
{
"content":"Hello, John! Welcome to Javapedia.net",
"_links":{
"self":{
"href":"http://localhost:8080/greeting?name=John"
}
}
}
Spring Profiles provide a way to segregate parts of your application configuration and make it be available only in certain environments. For example, swagger may be enabled only for lower environments and can be disabled for the production environment.
@Configuration @EnableSwagger2 @Profile("DEV,SIT,UAT") public class SwaggerConfig { // your swagger configuration }
Any @Component, @Configuration or @ConfigurationProperties can be marked with @Profile to limit when it is loaded.
Include starter dependencies spring-boot-starter-jdbc or spring-boot-starterdata-jpa and include a JDBC driver on classpath. Spring boot will configure the database with the properties defined in application.properties.
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:2001/mydb spring.datasource.username=username spring.datasource.password=password spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
Spring boot can even auto-configure connection pool given the jar provided in the classpath and properties set.
Configure Spring Security in the application. If Spring Security is on the classpath, then Spring Boot automatically secures all HTTP endpoints with "basic" authentication.
dependencies { ... compile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-security") ... }
Add the security configuration as shown below. Create WebSecurityConfig class annotated with @EnableWebSecurity to enable Spring Security's web security support and provide the Spring MVC integration. It also extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter and overrides a couple of its methods such as configure() method.
The configure(HttpSecurity) method defines which URL paths should be secured and which should not.
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService; import org.springframework.security.provisioning.InMemoryUserDetailsManager; @Configuration @EnableWebSecurity public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http .authorizeRequests() .antMatchers("/", "/home").permitAll() .anyRequest().authenticated() .and() .formLogin() .loginPage("/login") .permitAll() .and() .logout() .permitAll(); } @Bean @Override public UserDetailsService userDetailsService() { UserDetails user = User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder() .username("user") .password("password") .roles("USER") .build(); return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(user); } }
Swagger UI enables users to visualize and interact with the API's resources without having any of the implementation logic in place. It is automatically generated from your OpenAPI (formerly known as Swagger) Specification, with the visual documentation making it easy for back end implementation and client-side consumption.
Use exclude property to disable specific auto-configuration.
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude={DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
Reloading the changes without restarting the server is called hot swapping, Modern IDEs such as Eclipse, Intellij IDEA support hot-swapping of byte-code, so if you make a change that doesn't affect the class or method signatures it should reload cleanly with no side effects.
Any Spring @RestController in a Spring Boot application should render JSON response by default as long as Jackson2 is on the classpath.
HTTP response compression is supported by Jetty, Tomcat, and Undertow embedded containers. It can be enabled by adding server.compression.enabled=true in application.properties.
Spring Boot provides error mapping by default that handles all errors in a sensible way, and it is registered as a 'global' error page in the servlet container.
Spring Boot configures Spring MVC with a maximum file of 1MB per file and a maximum of 10MB of file data in a single request.
Spring Boot provides spring-boot-starter-data-jpa, which is one of the Spring Boot Starters, to easily connect relational database with Spring MVC applications.
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency>
You may use the exclude attribute with the annotation @SpringBootApplication.
@SpringBootApplication(exclude= {Employee.class}) public class AppConfiguration {}
- IP whitelisting restricts access from unauthorized resource.
- Run service endpoints in HTTPS in PROD environment.
- Enable CSRF tokens.
- Prevent XSS attacks by using content security policies.
- Always upgrade to the latest versions of dependencies.
- Use vulnerability monitoring tools such as snyk.
- Don't store passwords in plain text and use password hashing. Spring Security doesn't allow plain text passwords by default.
- Have your security Team perform code reviews periodically.
Mono and Flux are both reactive streams. A Mono is a stream of 0 to 1 element, whereas a Flux is a stream of 0 to N elements.
Spring Boot Admin is a community project from codecentric. Spring boot admin helps manage and monitor your Spring Boot applications. The spring boot apps register with Spring Boot Admin Client (through HTTP) or discovered using Spring Cloud (for example, Eureka, Consul). The UI is just a Vue.js application on top of the Spring Boot Actuator endpoints.
HttpMessageConverter is a strategy interface that specifies a converter that can convert from and to HTTP requests and responses.
By default, the following HttpMessageConverters are loaded by Spring.
- ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter that can read and write byte arrays.
- ResourceHttpMessageConverter can read/write Resources and supports byte range request.
- SourceHttpMessageConverter can read and write Source objects.
- StringHttpMessageConverter read and write strings.
- FormHttpMessageConverter read and write HTML forms.
Apache Tomcat is a Web Server and Servlet system which is open source (freely available on the internet). It is created by Apache Software Foundation.
Apache Tomcat is required to run Java Web Applications on the host and server based system. It runs JSP and Servlets within its web container.
Catalina is the inbuilt web container of Apache tomcat. It can be located in bin directory.
Catalina loads all the HTTP requests and instantiate the objects of GET and POST methods.
Embedded container let Spring Boot application run as a JAR directly from the command prompt without setting up a web server. Embedded container auto configure web server and run the application. But to run a WAR file, you need to first set up a web server like Tomcat which has Servlet container and then you need to deploy WAR to run the spring boot application.
Spring boot can control logging by specifying log levels on application.properties file.
Spring Boot uses Commons Logging for all internal logging and you can change log levels by adding following lines in the application.properties file.
logging.level.org.springframework.web=ERROR
logging.level.net.javapedia=DEBUG
The Spring Boot Maven Plugin provides Spring Boot support in Maven, packages executable jar or war archives and run an application "in-place".
The Spring Boot Plugin has the following goals.
- spring-boot:run runs/executes your Spring Boot application.
- spring-boot:repackage repackages your jar/war to be executable.
- spring-boot:start and spring-boot:stop to manage the lifecycle of your Spring Boot application (for example, for integration tests).
- spring-boot:build-info generates build information that can be used by the Actuator.
Default is 200 threads. The property is maxThreads.
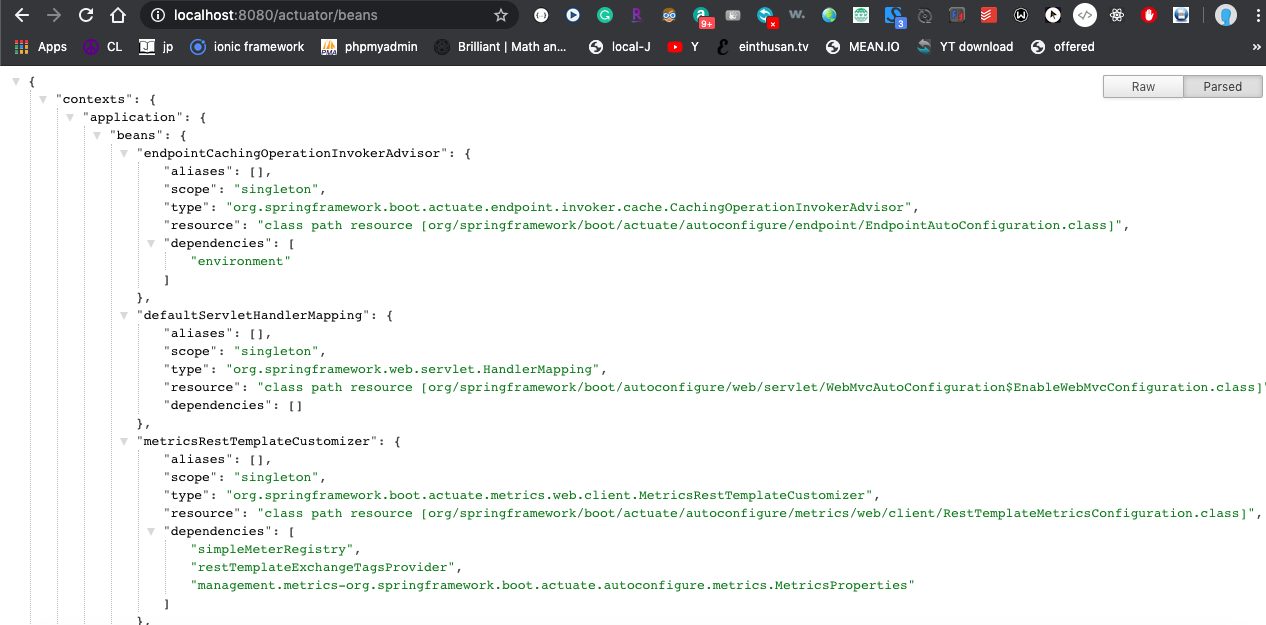
"beans" endpoint displays a complete list of all the Spring beans in your application.
| Spring. | Spring Boot. |
| Spring framework provides comprehensive infrastructure support for developing Java applications.. | Spring Boot is an extension of the Spring framework which eliminated the boilerplate configurations required for setting up a Spring application.. |
| Spring takes an unopinionated view. | It takes an opinionated view of the Spring platform which paved the way for a faster and more efficient development eco-system.. |
| Complex and more code/configuration than spring boot. | Less complex and less code in Spring Boot. |
Hibernate.
Relaxed binding maps the Environment property to the bean property name even it is not an exact match. For example, dash-separated environment properties (app-name bound to appName) or capitalized properties as in PORT (bound to port).
Spring boot supports relaxed binding.
@Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "host") public class ApplicationProperties { private String Name; private String PORT; private String app_name; @Override public String toString() { return "ApplicationProperties{" + "Name='" + Name + '\'' + ", PORT='" + PORT + '\'' + ", app_name='" + app_name + '\'' + '}'; } ... }
application.properties.
host.name=javapedia.net host.port=80 host.appName=JAVAPEDIA
In the above example, although the "host" bean property and configuration property name mismatch(appName vs app_name), the value is bound. For the complete example, take a look here.
Spring profiles provide a way to segregate parts of your application configuration, allows logical grouping of configurations based on environment and make it be available only in certain environments.
Spring Boot by default, creates the property file, application.properties. To create spring profiles based on environments, we will create different property files, one per environment.
application-DEV.properties,application-SIT.properties,application-PROD.properties, etc.
The application.properties file will still be active and acts as the parent of all env specific properties. In this file, we may specify which profile to activate by specifying in the property spring.profiles.active.
spring.profiles.active = DEV
| @SpringBootApplication. | @EnableAutoConfiguration. |
| @SpringBootApplication allows you to run the Main class as a JAR with an embedded container. It enables Java configuration, and it also enables Component Scanning. | @EnableAutoConfiguration enables automatic configuration features of the Spring Boot application, which to automatically configure your Spring application based on the jar dependencies that you have added. For example, If HSQLDB is on your classpath, and you have not manually configured any database connection beans, then we will auto-configure an in-memory database.. |
| SpringBootApplication combines of 3 annotations: @Configuration, used for Java-based configuration on Spring framework, @ComponentScan to enable component scanning of components, and @EnableAutoConfiguration itself, which is used to allow for auto-configuration in Spring Boot application. | Its primary task is to enable auto configuration. |
| allows excluding auto configuration. | EnableAuto configuration also allows exclusion. |
Spring Boot Maven Plugin plugin provides several goals to work with a Spring Boot application:
- Creates a jar or war file that is auto-executable,
- runs your Spring Boot application,
- integrate your Spring Boot application to the integration-test phase so that the application starts before it.
- generates build information that can be used by the Actuator.
@Value annotation can be used to access the property defined in the application.properties. @Value also can set a default value to use if the property is missing in the application.properties.
@Value("${host.name}") private String hostName;
Using default value,
@Value("${host.name:default-host}") private String hostName;
Using hard-coded value,
@Value("3.14") private String PI:
SpringApplication allows an application to be initialized lazily. When lazy initialization is enabled, beans are created as they are needed rather than during application startup.
This reduces the startup time and especially in web apps, the bean is not loaded until an HTTP request is received.
spring.main.lazy-initialization=true
Setting the property value to "true" leads to lazy initialization of all the beans in the application. This configuration affects all the beans in the context, use @Lazy(false) to exclude specific beans from lazy loading.
Lazy initialization is not enabled by default.
Yes. Spring Boot supports XML based configuration although it supports Java-based configuration.
To load XML configurations, create a @Configuration class and use @ImportResource annotation to load XML configuration files.
Spring boot has a starter for ActiveMQ known as "spring-boot-starter-activemq" can be added in your project build configuration as a dependency that provides default settings.
To configure your external ActiveMQ Broker, configure the ActiveMQ broker URL details in the spring.activemq.broker-url config in application.properties.
Most of the embedded servers and external servers support HTTP compression. It can be enabled by adding server.compression.enabled=true in application.properties.
| Endpoints. | Details. |
| env | This endpoint exposes properties from Spring Configurable environment. |
| health | Displays the health information of application. |
| shutdown | Allows the application to shutdown gracefully. |
| auditevents | exposes all audit event for the application. |
| metrics | displays "metrics" information about the application. |
| info | displays arbitrary application info. |
| caches | Exposes all the available caches. |
| beans | Lists all the spring beans available in your application. |
| httptrace | Exposes all the trace logs. It provides last 100 HTTP requests, by default. |
| threaddump | Performs thread dump of the application. |
| mappings | Returns the list of @RequestMapping paths in your application. |
| loggers | Displays the logger configuration and allows to modify. |
| scheduledtasks | Displays the scheduled tasks in your application. |
| heapdump | Returns an hprof heap dump file (applicable only for Spring web applications). |
Use exclude attribute of @EnableAutoConfiguration to specific auto-configuration classes that you do not want being auto-configured.
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude={DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class,SecurityAutoConfiguration.class})
if the class is not on the classpath, use the excludeName attribute of the annotation and specify the fully qualified name instead.
@EnableAutoConfiguration(excludeName={Employee.class})
You can also control the list of auto-configuration classes to exclude via the spring.autoconfigure.exclude property.
Spring boot automatically maps /src/main/resources/static as static resource folder. To add css or js, create subdirectories like /src/main/resources/static/css/ and /src/main/resources/static/js.
Batch processing involves the processing of large volumes of data. Spring boot batch provides reusable components, provides services and features for optimization and partition techniques, resulting in high volume and high-performance batch jobs.
Use spring-boot-starter-batch to implement batch processing in your spring boot application.
Maven:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-batch</artifactId> </dependency>
Gradle:
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-batch'
io.spring.dependency-management gradle plugin provides Maven-like dependency management functionality.
buildscript { repositories { maven { url 'https://repo.spring.io/plugins-snapshot' } } dependencies { classpath 'io.spring.gradle:dependency-management-plugin:1.0.7.BUILD-SNAPSHOT' } } apply plugin: "io.spring.dependency-management"
When you apply the io.spring.dependency-management plugin, Spring Boot's plugin will automatically import the spring-boot-dependencies bom from the version of Spring Boot that you are using. This provides a similar dependency management experience as in Maven. For example, it allows you to omit version numbers when declaring dependencies that are managed in the boom.
To use this, simply declare dependencies in the usual way but omit the version number:
dependencies { implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web' implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa' }
To enable SSL or HTTPS for your Spring Boot web application, place the certificate ( .p12 or .jks extension) under the resources folder, and define the server.ssl.* configuration in the application.properties.
server.port=8443 server.ssl.enabled=true server.ssl.key-alias=tomcatApp-localhost server.ssl.key-password=changeit server.ssl.key-store=classpath:keystore.jks server.ssl.key-store-provider=SUN server.ssl.key-store-type=JKS server.ssl.key-store-password=changeit
For yaml configuration, configure Spring Boot using the application.yml file located in the src/main/resources folder.
server:
port: 8443
ssl:
enabled: true
key-alias: tomcatApp-localhost
key-password: changeit
key-store: classpath:keystore.jks
key-store-provider: SUN
key-store-type: JKS
key-store-password: changei
@ConditionalOnBean annotation can be used to declare a condition. Only if the specified condition is satisfied then only bean will be added to the application context.
No.
@ConfigurationProperties support Relaxed binding & Metadata features while @Value doesn't.
@Value support SpEL evaluation while @ConfigurationProperties doesn't.
The "spring-boot-starter-parent" is a special starter that provides useful Maven defaults. It provides default configurations to your application and also the complete dependency tree to quickly build your Spring Boot project.
Default java version is 1.6. you may override this by specifying a property
Spring Boot Starter Parent specifies the default configuration for a host of plugins including maven-failsafe-plugin, maven-jar-plugin and maven-surefire-plugin.
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
ApplicationContext is the core interface, represents the Spring IoC container and is responsible for instantiating, configuring, and assembling the beans. ApplicationContext is responsible for bean factory methods for accessing application components, loading file resources, internalization, etc.
In Spring Boot ApplicationContext is created once we execute the SpringApplication.run() command.Spring Boot returns the ConfigurableApplicationContext which extends ApplicationContext.
@SpringBootApplication public class SpringBootAdminApplication implements CommandLineRunner { @Autowired private ApplicationContext applicationContext; public static void main(String[] args) { new SpringApplicationBuilder() .bannerMode(Banner.Mode.OFF) .sources(SpringBootAdminApplication.class) .run(args); } public void run(String... args) throws Exception { System.out.println("Application Context disp name=" + applicationContext.getDisplayName()); System.out.println("ID=" + applicationContext.getId()); System.out.println("Application name=" + applicationContext.getApplicationName()); String myBean = (String) applicationContext.getBean("myName"); System.out.println(("myBean Value=" + myBean)); } @Bean String myName() { return "javapedia.net"; } }
The application starts using the "main method" which calls the "run" method. From the run method, the main application context kicks off which searches for the classes annotated with @Configuration and initializes all the declared beans in those configuration classes. Based on the scope of those beans, stores those beans in JVM, specifically in a space inside JVM which is known as IOC container. After the creation of all the beans, automatically configures the dispatcher servlet and registers the default handler mappings, messageConverts, etc.
Both the Maven plugin and the Gradle plugin allow generating build information containing the coordinates, name, and version of the project.
build-info goal, as shown in the following example:
<build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.3.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT</version> <executions> <execution> <goals> <goal>build-info</goal> </goals> </execution> </executions> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
Gradle
springBoot {
buildInfo()
}
info and health are enabled by default. All others need to be enabled using configuration.
JSON Web Token (JWT) is an open standard (RFC 7519) that defines a compact and self-contained way of securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object. This information can be verified and trusted because it is digitally signed. The client will need to authenticate with the server using the credentials only once. During this time the server validates the credentials and returns the client a JSON Web Token (JWT). For all future requests, the client can authenticate itself to the server using this JSON Web Token (JWT) and so it does not need to send the credentials like username and password.
Spring Boot provides the following auto-configuration features for Spring MVC that works well with most applications.
- Inclusion of ContentNegotiatingViewResolver and BeanNameViewResolver beans.
- Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars.
- Automatic registration of Converter, GenericConverter, and Formatter beans.
- Support for HttpMessageConverters.
- Automatic registration of MessageCodesResolver.
- Static index.html support.
- Custom Favicon support.
- Automatic use of a ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer bean.
With Inbuilt Http Message conversion, we may implement minimal changes.
@PostMapping(path = "/mapJsontoXML", consumes = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE, produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE) public @ResponseBody RequestModel mapJsonToXML(@RequestBody final RequestModel request) { return request; }
"beans" endpoint is not enabled by default as it exposes certain sensitive information. However, for troubleshooting purposes, we can enable by configuration management.endpoints.web.exposure.include property in application.properties file or application.yaml.
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=info,health,beans
Start your application to access the actuator endpoints.
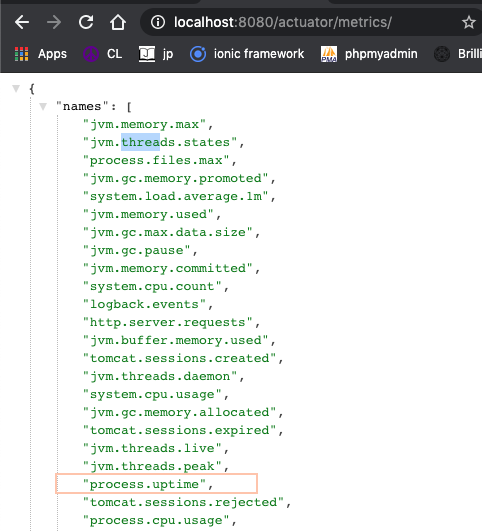
We may use "metrics" actuator endpoint. Spring Boot provides "metrics" endpoint that can be used diagnostically to examine the metrics collected by an application. The endpoint is not available by default and must be exposed.
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=info,health,metrics
When the application is up, access the metrics endpoint using http://localhost:8080/actuator/metrics/ (default). Navigating to /actuator/metrics displays a list of available meter names. You can drill down to view information about a particular meter by providing its name as a selector, e.g. /actuator/metrics/jvm.memory.max.
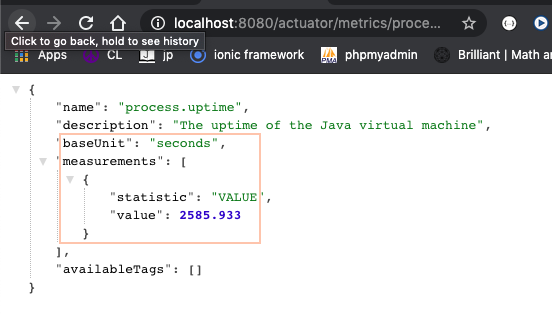
To access the process uptime, we may use the particular meter "process.uptime". Navigate to this particular meter using the URL : http://localhost:8080/actuator/metrics/process.uptime
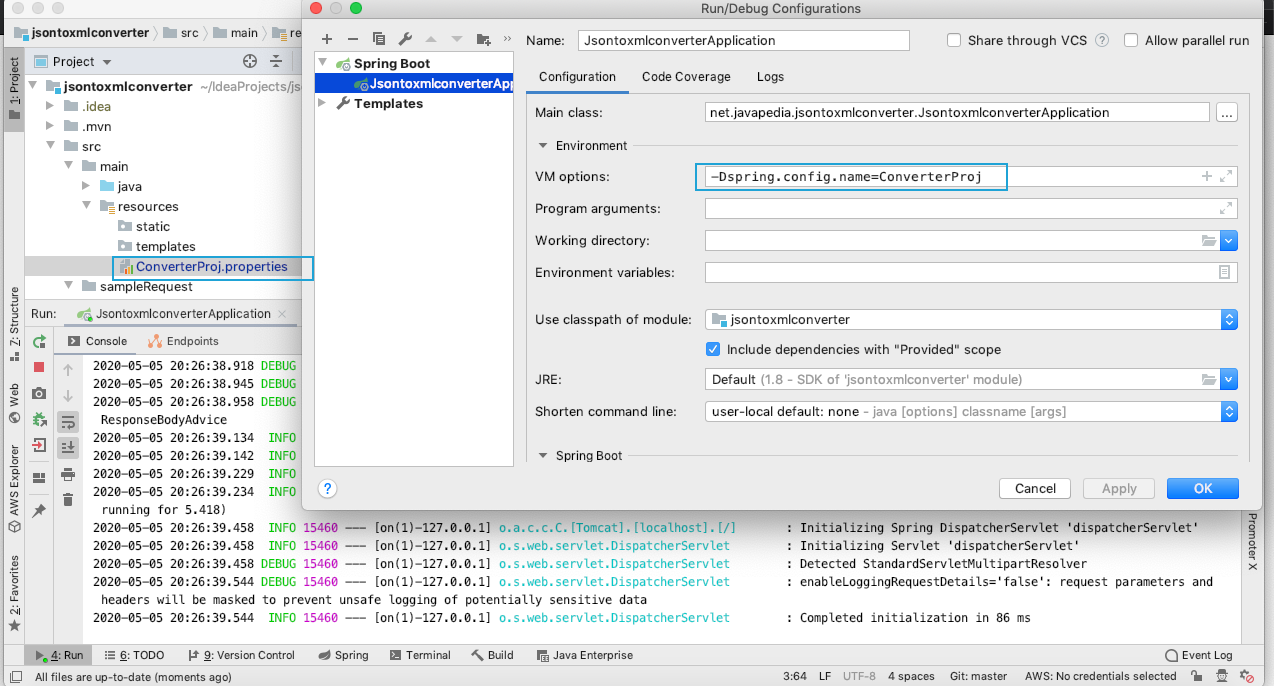
Rename tne application.properties as required, for example, ConverterProj.properties and specify the JVM parameter -Dspring.config.name=ConverterProj so that the properties loads from the properties file.
Spring Boot Application properties may contain sensitive information such as database passwords, MQ config details, CERT passwords. The password stored in the application properties is not recommended to be PLAIN-TEXT and needs to be encrypted.
#Plain password not recommended app.mysql.password=My-plain-password
Spring boot doesn't provide inbuilt support for encryption. You may use Jasypt library to encrypt properties, so you could have your property like this:
#Encrypted using Jasypt app.mysql.password=ENC(XcBjfjDDjxeyFBoaEPhG14wEzc6Ja+Xx+hNPrJyQT88=)
Using Jasypt, you will encrypt your DB password using a master password which will be supplied to the application when starting to decrypt on the fly.
The @ConditionalOnMissingBean annotation is a spring conditional annotation for registering beans only when they are not already in the application context.
@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(SomeBean.class) public SomeBean otherBean(){ return new SomeBean(); }
The above bean will get loaded by Spring only if there is no other bean of this type present in the context. On the other hand, if there is already a bean of the type SomeBean present in the application context, the above bean will not be created.
Use cases:
Specifying a fallback bean which gets only loaded as backup/default if there is no bean of the same type present. The classical example would be using an in-memory database if there is no real database configured.
Specifying a default bean which allows being overridden in the case that a more specific bean of the same type is present in the context. One of the examples would be using a default authentication mechanism unless someone decides to replace it with his own custom authentication.
Spring provides an easy way to handle exceptions using ControllerAdvice annotation. We handle all exceptions thrown by the controller class by implementing a ControlerAdvice class.
Spring 3.2 brings support for a global @ExceptionHandler with the @ControllerAdvice annotation that enables a mechanism that deviates from the older MVC model of the exception handling and makes use of ResponseEntity along with the type safety and flexibility of @ExceptionHandler.
@ControllerAdvice public class RestResponseEntityExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler { @ExceptionHandler(value = { EntityNotFoundException.class, MyCustomException.class, IllegalArgumentException.class, IllegalStateException.class }) protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleConflict( RuntimeException ex, WebRequest request) { String bodyOfResponse = "Exception occurred somewhere at the application level"; return handleExceptionInternal(ex, bodyOfResponse, new HttpHeaders(), HttpStatus.CONFLICT, request); } }
Add Jackson XML extension (Jackson-dataformat-XML) on the classpath, it will be used to render XML responses.
The @ImportResource annotation is used to import one or more XML configuration files containing bean definitions.
We can run Spring Boot inside docker by defining "Docker image" using Dockerfiles. Dockerfiles are a manifest of commands used to build and configure our docker container. To configure our Docker image to run our Spring Boot application, we will want to:
- Install latest CentOS (OS) image from Docker Hub.
- Install and configure Oracle Java.
- Install the Spring Boot artifact: our executable JAR file.
- Run the Spring Boot application.
Cloud Foundry is a PaaS (Platform as a Service) service where we can easily deploy and manage our spring/spring boot applications and the Cloud Foundry will take care of the rest of the cloud-based features like scalability, high availability, etc.
Spring Boot provides a number of utilities and annotations to help to test your application.
Use the spring-boot-starter-test "Starter", which imports both Spring Boot test modules (spring-boot-test and spring-boot-test-autoconfigure) as well as other below libraries.
- spring-boot-test, a spring boot test module that contains core items.
- spring-boot-test-autoconfigure, a spring boot test module that supports auto-configuration for tests.
Other libraries include,
- JUnit 4, the de-facto standard for unit testing Java applications.
- Spring Test & Spring Boot Test provide utilities and integration test support for Spring Boot applications.
- AssertJ, a fluent assertion library.
- Hamcrest, a library of matcher objects (a.k.a constraints or predicates).
- Mockito, Java mocking framework.
- JSONassert, assertion library for JSON.
- JsonPath, XPath for JSON.
CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) is a mechanism implemented by browsers and helps users to authorize cross-domain requests. This mechanism serves as an alternative to less secure and less powerful hacks of the kinds of IFrame or JSONP.
To create SOAP web service, we need spring-boot-starter-web-services as following.
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web-services</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>wsdl4j</groupId> <artifactId>wsdl4j</artifactId> </dependency>
To create SOAP client use the below dependencies.
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.ws</groupId> <artifactId>spring-ws-core</artifactId> </dependency>
Response Entity is an HTTP response object that includes headers,status code and payload/body of your response.
There are 4 primary components of a Blockchain ecosystem:
- Node application,
- Shared ledger,
- Consensus algorithm,
- and Virtual Machine.
Spring Boot Framework supports CORS and offers different ways to configure.
- Global CORS configuration: When a global CORS configuration needs to be defined with annotation-based, fine-grained configurations, then the same has to be declared in Spring MVC and combined with @CrossOrigin configuration using filters. The GET, POST and HEAD methods, and all origins are permitted by default in this method of enabling CORS in Spring Boot.
- The Controller method of CORS configuration: The @CrossOrigin annotation can be added to the @RequestMapping handler method to enable CORS in Spring Boot. The @CrossOrigin allows all the HTTP methods and origins specified in @RequestMapping annotation.
Docker is a software platform for building applications based on containers, small and lightweight execution environments that make shared use of the operating system kernel but otherwise run in isolation from one another.
Docker is an open source project launched in 2013.
Docker enables you to deploy a server environment in containers. A container is a unit of software that assembles code, provide runtime, inject dependencies, configure settings, and initialize the entire app in a single package that you can run reliably from one computing environment to another.
Spring boot leverage docker functionality and achieves scalability.
Spring boot provides,
- single, independent executable JAR packaging with required dependencies.
- production-ready services for building microservices.
- actuator, that facilitates health check of the application and monitoring.
- embedded, pre-configured servers like tomcat.
- less development effort.
- minimal configuration overheads and can be customized for meeting the development needs of microservices.
To register an auto-configuration class, you must have its fully-qualified name listed under the EnableAutoConfiguration key in the META-INF/spring.factories file:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=net.javapedia.autoconfigure.CustomAutoConfigurationExample
When running integration tests for a Spring application, we must have an ApplicationContext.
Spring Boot provides a special annotation for testing @SpringBootTest. This annotation creates an ApplicationContext from configuration classes indicated by its classes attribute.
Spring Boot searches for the primary configuration class when classes attribute not set. The search starts from the package containing the test up until it finds a class annotated with @SpringBootApplication or @SpringBootConfiguration.
Shutdown is an endpoint that allows the application to be gracefully shutdown. This feature is not enabled by default. You may enable this by using management.endpoint.shutdown.enabled=true in your application.properties file.
We can use the application.properties to configure the web application type to disable web server.
spring.main.web-application-type=none
Spring @Profile allow developers to register beans by condition. For example, register beans based on what operating system (Windows, Linux/Unix) your application is running, or load database properties file based on the application running in development, test, staging or production environment. Similarly, we can register beans conditionally on cloud vs non-cloud environment.
In Spring Boot, data validation can be performed using various mechanisms. One common approach is to use the validation annotations provided by the Bean Validation API, such as @NotNull, @Size, and @Pattern, on the fields of model objects.
By including the necessary validation annotations, Spring Boot automatically validates the input data and generates validation errors. These errors can be handled using BindingResult or Errors objects. Additionally, custom validation logic can be implemented by creating custom validation classes and methods.
The @TransactionalEventListener annotation in Spring Boot lets you listen to transactional events and perform actions based on those events. You can use this annotation on methods that should be invoked when a specific transactional event occurs such as before or after a transaction is committed or rolled back.
The @TransactionalEventListener annotation provides a convenient way to handle domain-specific logic or side effects based on transactional events in a Spring Boot application.
The @ModelAttribute annotation is used in Spring Boot to bind request parameters or form data to method parameters or model attributes. It can be applied to method parameters or method return values.
When applied to method parameters, the @ModelAttribute annotation binds the incoming request parameters or form data to the corresponding method parameters. When applied to method return values, it binds the method's return value to a model attribute, making it available in the view for rendering.
You can change log levels in a running Spring Boot application without a restart
using the Spring Boot Actuator's /actuator/loggers endpoint.
This allows you to dynamically view and modify logging configurations via a simple HTTP request.
Steps to Implement and Use Dynamic Logging
1. Add the Actuator Dependency
Include the Spring Boot Actuator dependency in your project's
pom.xml (Maven) or build.gradle (Gradle) file.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
2. Expose the Loggers Endpoint
To expose the loggers endpoint, configure
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include
in your application.properties or application.yml file.
3. Change Log Levels at Runtime
Use GET requests to view current logger levels and POST requests to change them.
View current logger levels:
GET http://localhost:8080/actuator/loggersChange a specific logger level:
POST /actuator/loggers/{name}
{
"configuredLevel": "DEBUG"
}
Setting configuredLevel to null resets the logger to its default level.
Important Considerations
- Security: Secure Actuator endpoints, especially in production, due to the sensitive nature of the information and control they provide.
- Persistence: Changes made via Actuator are temporary and will be lost on application restart.
- Centralized Management: Consider tools like Spring Boot Admin for managing log levels across multiple microservice instances.
HttpServletRequest is part of the standard Java Servlet API, designed for use in traditional, thread-per-request servlet containers. ServerHttpRequest is an abstraction introduced by the Spring Framework, primarily for use in reactive programming environments (like Spring WebFlux), which is not tied to the Servlet API's thread model.
| Feature | HttpServletRequest | ServerHttpRequest |
|---|---|---|
| Framework/API | Standard Java Servlet API (javax.servlet.http or jakarta.servlet.http) | Spring Framework abstraction (org.springframework.http.server or .reactive) |
| Programming Model | Synchronous, blocking, thread-per-request model | Asynchronous, non-blocking, reactive model (WebFlux) |
| Thread Management | Uses a dedicated thread to handle the entire request life cycle | Can switch threads during processing for efficiency; not thread-aware in the same way as servlets |
| Purpose | Provides request information for HTTP servlets (e.g., doGet, doPost) | Provides a generic abstraction over server-side HTTP, allowing Spring to run on different platforms (Servlet, Netty, etc.) |
| Relationship | Extends the generic ServletRequest interface | Is an interface with specific implementations (e.g., ServletServerHttpRequest wraps an HttpServletRequest when running on a servlet container) |
