BigData / Splunk Interview Questions
Machine data, sometimes called machine-generated data, is the digital information that is automatically created by the activities and operations of networked devices, including computers, mobile phones, embedded systems, and connected wearable products. In a wider context, machine data can also include information generated by websites, end-user applications, cloud-deployed programs, servers, etc.
Splunk Enterprise takes valuable machine data and turns it into powerful operational intelligence.
- Index data,
- Search & Investigate,
- Add knowledge to the data by categorization and enriching,
- Monitor & Alert,
- Report & Analyse.
There are 3 components.
- Indexer,
- Search Head, allows the users to use Splunk Search language.
- and Forwarder, are Splunk enterprise instances that consume data and forward to indexers for processing.
Yes.
Forwarders.
Splunk roles determine what a user is able to see, do and interact with.
There are 3 main splunk roles.
- Admin role is the most powerful, allows to install apps and create knowledge objects for all the users.
- Power role can create and share knowledge objects for users of an app and do realtime searches.
- User role will only see their own knowledge objects and those shared with them.
Two apps will be available, Home App and Search & Reporting App.
Indices are organized hierarchical directories in which data is categoried and stored.
Yes.
Commands that create statistics and visualizations are called transforming commands.
Not, OR and AND. To control the evaluation use parentheses.
Knowledge object is a user-defined entity that enriches the existing data in Splunk Enterprise. You can use knowledge objects to get specific information about your data. When you create a knowledge object, you can keep it private or you can share it with other users.
Yes but field values are NOT.
- Using time (limit : earliest and latest) to narrow down the amount of data to search.
- Use inclusion to search rather than exclusion, for example, using status = failed is better than status !=success.
- fields, specifies fields to be included/excluded in the result.
- table, specifies result in tabular format.
- rename, allows to rename fields.
- dedup, remove duplicate values in a field.
- and sort command, allows sorting by fields and we can also specify limit.
The top command is a transforming command that finds the most common values of a given field.
index=sales sourcetype=vendor_sales | top Vendor limit=10
The rare command has the same options as the top command except that it shows the least common values of a field set.
Admin, Power and User roles.
Data models are knowledge objects that provide the data structure that drives Pivots. These are created by Admin and Power role who has knowledge of Search language and solid understanding of the data.
- Fast mode for performance,
- Verbose for completeness and more details,
- Smart mode for combination of performance and additional details.
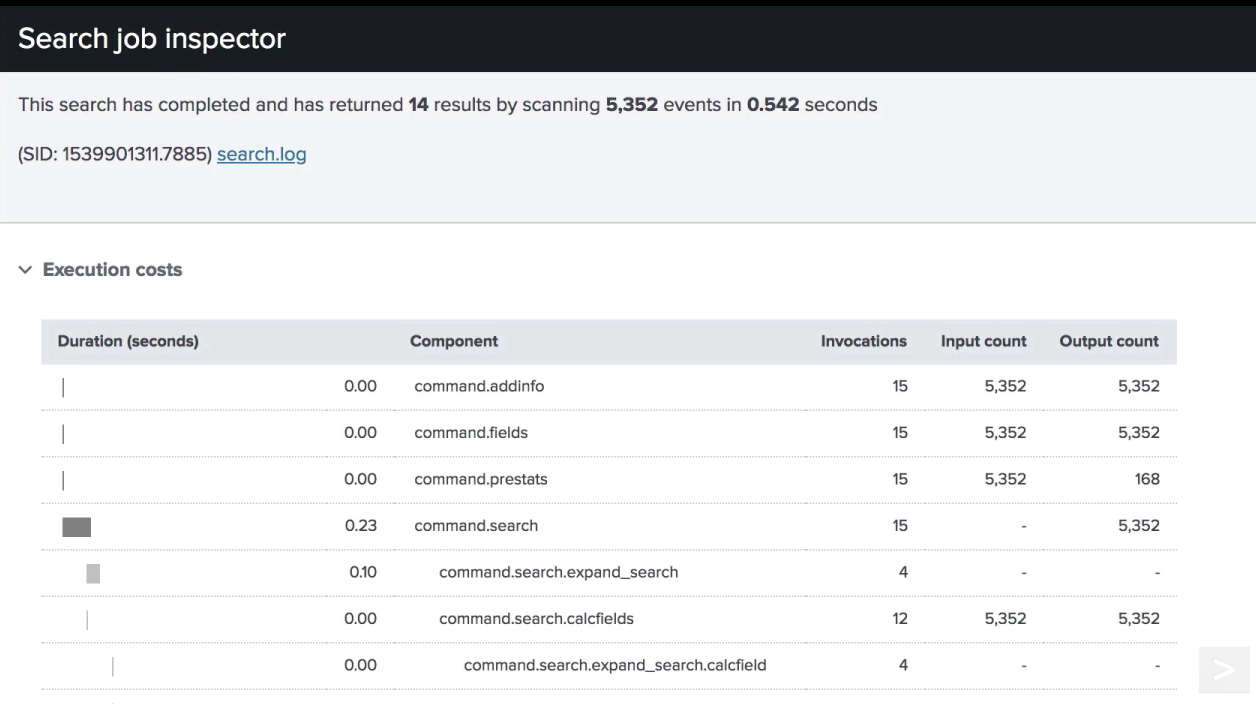
Search Job Inspector determines which phase of a search takes the most time. It dissects the behavior of searches to help understand costs. Any search job that has not expired can be inspected.
Iplocation command lookup and add location information to events.
Geostats command aggregates geographical data for use on a map visualization.
index=sales sourcetype=vendor_sales | geostats latfield=VendorLatitude longfield=VendorLongitude count by product_name
Splunk supports 3 types of search modes.
- Fast mode,
- Smart mode,
- and Verbose mode.
